What is an Asset Administration Shell?
Industry 4.0 promises more efficient and sustainable manufacturing processes through digitalization. The foundation for this is a seamless, automatic exchange of information between systems and products. This is where the Asset Administration Shell (AAS) comes into play.
An Asset Administration Shell is a vendor-independent standard for describing digital twins. Basically, it is the digital representation of an asset; either a physical product or a virtual object (e.g., documents or software).
The AAS defines the appearance of the asset in the digital world. It describes which information of a device is relevant for communication and how this information is presented. This means the AAS can provide all important data about the asset in a standardized and automated way.
Let us take a look at a practical application to understand the benefits of an AAS:
Use case: AAS as enabler for new services
As part of the ESCOM research project, CONTACT Software collaborates with GMN Paul Müller Industrie GmbH & Co. KG to implement AAS-based component services. The family-run company manufactures motor spindles which are installed by its customers as components in metalworking machine tools and then resold.
Before the project began, GMN had already developed a new sensor technology. It enables deep insights into the behavior of a spindle and provides information on overall operation of the spindle system. The company wants to use this data to offer new, product-related services:
- Certified commissioning: Before GMN ships its spindles, the components are put through a defined test cycle on the company’s in-house test bench. GMN uses the data from this reference cycle to ensure that motor spindles are installed and commissioned correctly at the customer’s facility.
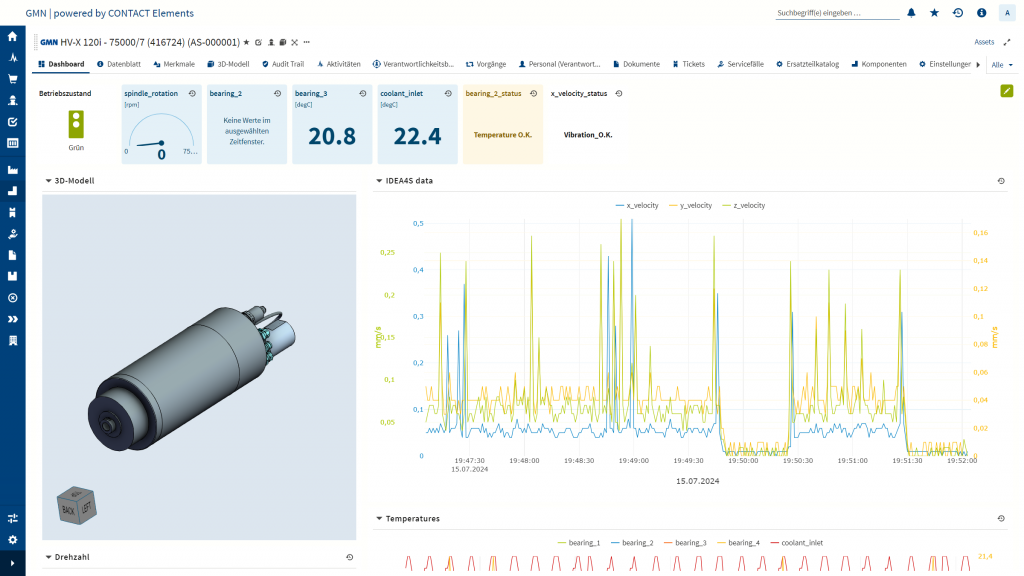
- Predictive services: Using the IDEA-4S sensor microelectronics, customers shall be able to continuously record and analyze operating data that provide insights into the availability and operation of the spindles. If necessary, the data can be shared with GMN, for example, for problem analysis. This saves valuable time until the machine is back up and running. In the future, GMN will be able to offer smart predictive services like predictive maintenance.
About GMN Paul Müller Industrie GmbH
GMN Paul Müller Industrie GmbH & Co. KG is a family-owned mechanical engineering company based in Nuremberg, Germany. It produces high-precision ball bearings, machine spindles, freewheel clutches, non-contact seals, and electric drives that are used in various industries. The company manufactures most of these components individually for its customers on site and sells its products via a global sales network.
How do we realize the new services?
To provide such services, companies must be able to access and analyze the sensor data of their machines. Furthermore, machines (or their components) must be enabled to communicate independently with other assets and systems on the shopfloor.
For both tasks, GMN uses CONTACT Elements for IoT. The modular software not only helps the company to record, document and evaluate the reference and usage data of their spindles. It also includes functions that enable users to create, fill and manage the AAS for an asset.
Background
During the implementation of services based on spindle operating data, GMN benefits from the cooperation with a customer. This company installs the spindles in processing machines that GMN uses to manufacture its own products. As a result, GMN can gather the operating data in-house and use it to improve the next generation of spindles.
What role does the AAS play?
For the components to exchange information in a standardized form, an AAS must be created for the spindle at item and serial number level. This is also done using CONTACT Elements for IoT. The new services are mapped in a so-called AAS metamodel. It serves as a “link” to the service offers.
AAS and submodels
The AAS of an Industry 4.0 component consists of one or more submodels that each contain a structured set of characteristics. These submodels are defined by the Industrial Digital Twin Association (IDTA), an initiative in which 113 organizations from research, industry and software (including CONTACT Software) collaborate to define AAS standards. A list of all currently published submodels is available at https://industrialdigitaltwin.org/en/content-hub/submodels.
In CONTACT Elements for IoT, GMN can populate the AAS submodels with little effort. The platform includes a widget developed as a prototype during the research project. It provides an overview of which submodels currently exist for the asset and which are available but not yet created. Through the frontend, users can jump directly to the REST node server and upload or download submodels (in AAS/JSON format).
During the implementation of data-driven service offerings, GMN focuses on the submodels
- Time Series Data (e.g., semantic information about time series data)
- Digital Nameplate (e. g., information about the product, the manufacturer’s name, as well as product name and family),
- Contact Information (standardized metadata of an asset) and
- Carbon Footprint (information about the carbon footprint of an asset)
Filling the submodels is simple. This is demonstrated by the module Time Series Data. During the reference run of a motor spindle on the in-house test bench, the time series data is recorded by CONTACT Elements for IoT. The platform automatically transfers this data to the AAS submodel of the motor spindle being tested. At the same time, the platform creates a document for the reference run. This allows GMN to track its validity at any time and make it available to external stakeholders.
New services on the horizon
Using Asset Administration Shells allows GMN to realize its service ideas. This currently concerns the commissioning service and automated quality assurance services.
By analyzing the spindle data, the company can identify outliers in the operating data and make suitable recommendations for action. For example, different vibration velocities indicate an incorrect installation of the spindle in the machine or that time-varying processes are occurring. The analysis can also be used to provide insights about anomalies in operating behavior.
Dashboards in CONTACT Elements for IoT increase transparency. They provide GMN with all relevant information about the spindles on the test bench, from 3D models to status data. This overview is extremely valuable, particularly for quality management.
Summarized
Asset Administration Shells are vendor-independent standards for describing digital twins. They are among the most important levers for implementing new Industry 4.0 business models, as they enable communication between assets, systems, and organizations. The example of GMN demonstrates the practical benefits of the AAS. The company uses it to design new, product-related services based on information from the AAS of its products. GMN can successively improve these services by continuously analyzing operating data in CONTACT Elements for IoT.