Pontus-X is a core ecosystem within Gaia-X. It was one of the first publicly available Gaia-X ecosystems with a large number of participating projects and companies from multiple countries. This has made it a crucial catalyst for the development and deployment of Gaia-X technologies. By connecting CONTACT Elements to Pontus-X, we enable federated data exchange that boosts operational efficiency and improves data governance. In this article, learn how companies can operate confidently in a world of distributed data.
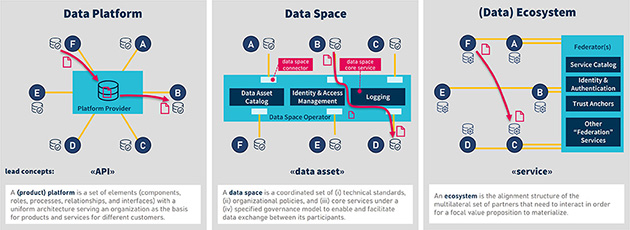
Technically, Pontus-X is built on Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) for the decentralized and trustworthy management of data and services. A key element of Pontus-X is the Ocean Protocol by Ocean Protocol Foundation, which puts data control in the hands of data owners and service providers.
One of Pontus-X’s most relevant features for ensuring data sovereignty is Compute-to-Data.
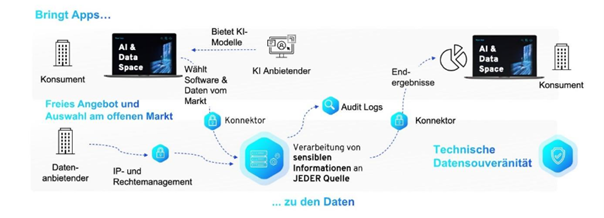
With the help of Compute-to-Data, data never leaves its owner’s infrastructure, thus remaining more effectively under their control. Instead, it allows algorithms to be brought to the data, extracting valuable insights without revealing the data itself. One exemplary use case is Federated Learning, which involves training AI models with distributed data. In this process, users receive only the trained model but no direct access to the sensitive training data.
Through this combination of various technologies, Pontus-X provides a solid foundation for secure, transparent, and sovereign data exchange within the Gaia-X ecosystem.
CONTACT Elements: Your data in Gaia-X
CONTACT Elements enables companies to seamlessly integrate their data into the Gaia-X ecosystem. A practical example is our partner GMN, a leading manufacturer of high-tech motor spindles. GMN uses sensor data from its spindles to offer data-driven services.
We’ve integrated CONTACT Elements to link quality data from a spindle on the shopfloor with the results of an end-of-line test bench. This data allows GMN to offer its customers comprehensive data-driven services, such as verifying correct assembly or performing digital commissioning.

We realized this data offering through the Pontus-X ecosystem. CONTACT Elements collects the relevant data from the spindles, aggregates it, and publishes it in the Pontus-X ecosystem. This process is largely automated and uses the AAS integration module as well as the data space integration of the Elements platform.
Through this integration, we empower companies like GMN to securely, reliably, and sovereignly share their data in order to develop new business models and innovative services.
Federated data exchange: Added value for your business
Federated data exchange offers significant advantages to companies. Unlike centralized platforms, data remains at its original storage location. Each organization retains control over its own data and determines who can access which data.
Increased operational efficiency:
- Faster data availability: Access to real-time data without long transfer times or complex integration projects accelerates decision-making processes and responses to market changes.
- Improved collaboration: Secure and controlled data exchange supports cooperation with partners, suppliers, and customers. This leads to more efficient processes, shorter lead times, and higher quality.
- Process automation: Automated data exchange between different systems and organizations reduces manual tasks and errors.
Improved data governance:
- Transparent data origin: Understanding data provenance is particularly important for companies operating in regulated industries or those that need to meet strict compliance requirements.
- Controlled data access: Companies retain control over who can access their data and how it is utilized. This enables them to protect sensitive data and adhere to data protection regulations.
- Meeting compliance requirements: Federated data exchange supports companies in meeting compliance requirements by ensuring adherence to defined rules and guidelines for data exchange.
Specific use cases:
- Supply chain management: Data exchange between suppliers, manufacturers, and logistics providers enables transparent and efficient supply chain management.
- Engineering: The exchange of design data between various engineering departments or external partners accelerates the development process and improves product quality.
- Production: Exchanging production data between different production sites enables more efficient resource utilization and optimizes production planning.
Our approach: “Bring your own connector”
Building and operating proprietary infrastructure can be complex. That’s why we support companies with our “bring your own connector” approach, which adheres to the Gaia-X principle of portability. This avoids vendor lock-in by giving companies the freedom to choose which connector they integrate into their existing or new infrastructure and where they operate it.
What CONTACT Elements offers:
- Integration into existing infrastructures: CONTACT Elements focuses on seamless integration into existing or new infrastructures required for participation in Gaia-X.
- Interfaces to various data spaces: Whether it’s Pontus-X or Eclipse Dataspace Components (EDC), CONTACT Elements provides interfaces to both technologies. This allows companies the flexibility to choose which data space best suits their needs.
With our “bring your own connector” approach, companies leverage the benefits of the Gaia-X ecosystem without compromising on flexibility, portability, or data sovereignty.
CONTACT Elements paves the way for sovereign data exchange in the Gaia-X ecosystem
The vision of Gaia-X to create an open, secure, and trustworthy data ecosystem is drawing closer. By connecting CONTACT Elements to Pontus-X and through the “bring your own connector” approach, we give companies the flexibility and portability they need.
Federated data exchange offers companies a multitude of benefits: from increasing operational efficiency and improving collaboration to unlocking new business models.
We are convinced that Gaia-X has the potential to fundamentally transform the European economy and drive innovation across all industries. With CONTACT Elements, companies are well equipped to seize these opportunities and actively shape the future of data exchange.