The evolution of language models in the field of NLP (Natural Language Processing) has led to huge leaps in the accuracy of these models for specific tasks, especially since 2019, but also in the number and scope of the capabilities themselves. As an example, the GPT-2 and GPT-3 language models released with much media hype by OpenAI are now available for commercial use and have amazing capabilities both in type, scope, and accuracy, which I will discuss in another blog post. This was achieved in the case of GPT-3 by training using a model with 750 billion parameters on a data set of 570 GB. These are jaw-dropping values.
The larger the models, the higher the cost
However, the costs of training these models are also gigantic: Taking only the stated compute costs 1 for a complete training run, the total amount for training GPT-3 is 10 million USD 2, 3. In addition, there are further costs for pre-testing, storage, commodity costs for deployment, etc., which are likely to be in a similar amount. Over the past few years, the trend of building larger and larger models has been consistent, adding about an order of magnitude each year, i.e., the models are 10x larger than the year before.
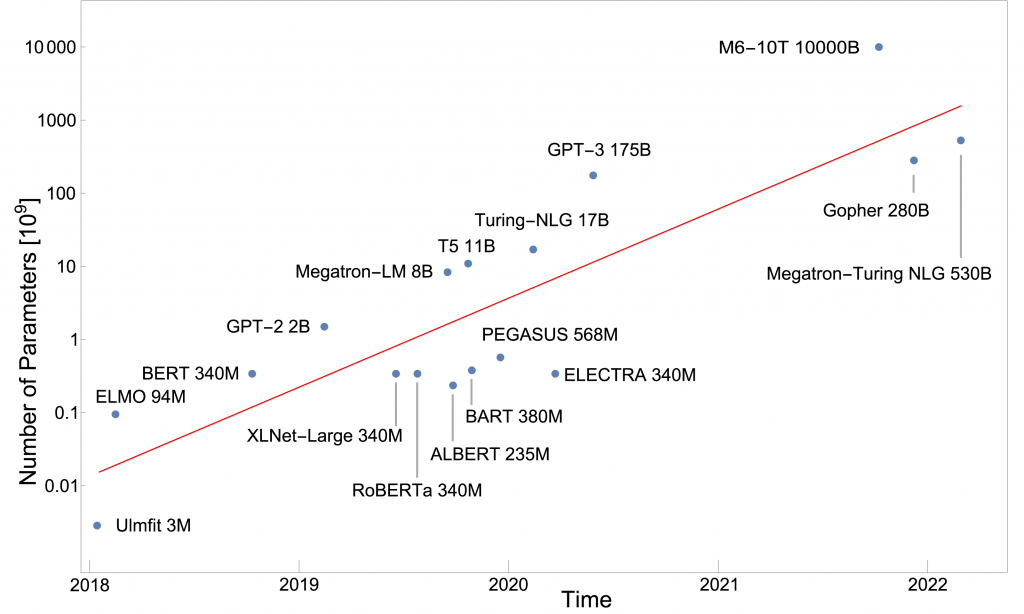
The next model of OpenAI GPT-4 is supposed to have about 100 trillion parameters (100 x 1012 ). For comparison, the human brain has about 100 billion neurons (100 x 109) which is 1000 times less. The theoretical basis for this gigantism is based on studies which show a clear scaling behavior between model size and performance 4. According to these studies, the so-called loss – a measure for the error of the predictions of the models – decreases by 1, if the model becomes 10 times larger. However, this only works if the computing power and the amount of training are also scaled upwards.
In addition to the enormous amounts of energy required to calculate these models and the associated CO2 footprint, which is assuming worrying proportions, there are direct economic consequences: Apparently, not only smaller companies cannot afford the cost of training such models, but also larger corporations are likely to balk at costs of $10 million, or $100 million or more in the future. Not to mention the necessary infrastructure and staffing for such an endeavor.
Monopoly position of the big players
This has a direct impact on availability: while the smaller models are now open source until the end of 2019 and can be freely accessed via specialized providers, this no longer applies to the larger models from around the end of 2020 (the appearance of GPT-2). OpenAI, for example, offers a commercialized API and only grants access through an approval process. On the one hand, this is convenient for developing applications with these NLP models, as the work of hosting and administration is eliminated; on the other hand, the barrier to entry for competitors in this market is so steep that essentially the super-big AI companies participate there: Google with OpenAI, Microsoft with Deepmind, and Alibaba.
The consequences of these monopoly positions of the leading AI companies are, as with every monopoly, pricing models without alternatives and rigid business practices. However, the capabilities of the current large language models such as GPT-3 and Megatron Turing NLG are already so impressive that it is foreseeable that in 10 years every company will probably need access to the current models for the most varied applications. Another problem is that the origin of the models from the American or Chinese area brings a large bias into the models, which on the one hand is clearly expressed in the fact that English or Chinese is the language with which the models work best. On the other hand, the training datasets that come from these cultural areas bring with them the very cultural tendencies from these spaces, so it is to be expected that other regions of the world will be underrepresented and continue to fall behind..
What can be done?
In my opinion, it is important to keep a careful eye on the development and to be more active in shaping the development of AI in the European area. In any case, a greater effort is needed to avoid dependence on monopolized AI providers in the long term. It is perhaps conceivable to involve national computing centers or research alliances that, united with companies, train and commercialize their own models and form a counterweight to American or Chinese companies. The next 10 years will be decisive here.
1 See here in section D as well as compute costs per GPU e.g. on Google Cloud approx. 1USD/hour for an NVIDIA V100
2 Calculation approach: V100 = 7 TFLOPs = 7 10^12 / s, 3.14 10^23 flops => 3.14 10^23/7×10^12 / 3600 = 10^7 hours = 10 million USD, details of the calculation and research of the parameters here.
3 see also here for comparison graph with older data.
4 see arxiv and Deepmind