ESG compliance is no longer a nice-to-have. It has become essential for competing in an increasingly sustainability-conscious market, saving resources and costs, and meeting ever-stricter regulatory requirements. Regulations such as the European Commission’s Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) or the Supply Chain Act require companies to report ESG data transparently. While many organizations still rely on document-centric approaches and struggle with isolated solutions, a strategic competitive advantage is emerging elsewhere: product-centric ESG reporting.
What is ESG reporting?
Sustainable business practices have many facets. The ESG approach breaks them down into three core dimensions:
• E = Environmental
• S = Social
• G = Governance
In an ESG report, companies provide information on all three areas. This includes data such as CO2 footprints, energy consumption in production and operations, as well as information on promoting biodiversity and reducing waste. It also covers aspects like compliance with fair labor conditions and human rights, ensuring diversity, implementing effective risk management and compliance practices.
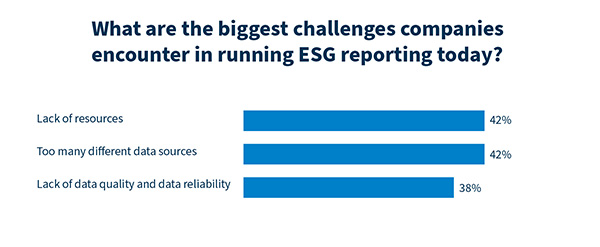
Data management is key in ESG reporting
This data – especially environmental KPIs – are often scattered across multiple sources: internal IT tools, external environmental databases, or supplier and partner systems. For many companies, preparing an ESG report therefore comes down to one central question: How can reliable ESG data from diverse sources across the entire value chain be collected and analyzed?
One key solution lies in anchoring ESG reporting directly within product development – specifically, in the PLM system. This is where crucial data across the entire product lifecycle is stored: information about the product portfolio, the materials used and their sourcing, emissions from production and the supply chain, as well as data from later lifecycle phases such as use, disposal, and recycling. With this structured and traceable data foundation, a PLM system provides the ideal basis for a precise, transparent, and strategically valuable sustainability assessment.
Product-centric single source of truth as an enabler
An open integration platform like CONTACT Elements offers another crucial advantage for ESG reporting: it seamlessly incorporates information from a variety of internal and external sources. Through APIs, it exchanges data with third-party systems such as ERP tools. Supply chain information can be integrated via standardized exchange formats like the Asset Administration Shell (AAS) or data ecosystems (such as Pontus-X or Catena-X). This makes the platform a single source of truth for company-wide ESG reporting.
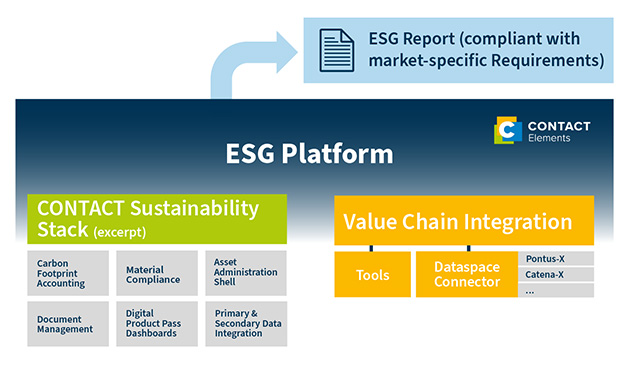
Ideally, such a solution comes with built-in capabilities to assess and analyze the data. For example, CONTACT Elements uses AI methods to evaluate data quality. In the next step, powerful modules – such as for calculating the Product Carbon Footprint – then generate a compliant ESG report. This creates a comprehensive, audit-ready reporting that meets all market-specific requirements.
From ESG reporting to a sustainability strategy
Companies that rely on product-centric, integrated solutions like CONTACT Elements don’t just tackle the mandatory task of ESG reporting – they have the chance to strategically embed sustainability across the organization. For example, ESG data in CONTACT Elements can be directly linked to product structures and development processes. This allows developers to make early assessments of potential CO2 emissions across the product portfolio or in specific manufacturing processes, and to optimize them in a targeted way.
The result: sustainable innovations, more attractive products, streamlined processes, and lower costs. The foundation for this is always a software platform like CONTACT Elements: open, scalable, and equipped with powerful business applications.
Learn in this article by consulting firm CIMdata how companies can systematically embed sustainability in PLM to reduce their environmental impact across the entire product lifecycle.

